ans.
 |
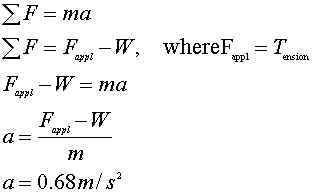 |
Newton's Laws
Next Assignment Worksheet(1-10)
pg 107 (21-29)
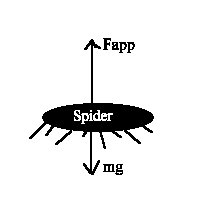
21. A 0.00021kg spider is suspended from a thin strand of spider web. The greatest tension the strand can withstand without breaking is 0.0022N. What is the maximum acceleration with which the spider can safely climb up the strand?
ans.
22. A sled of mass 50kg is pulled along snow-covered, flat ground. The static friction coefficient is 0.30, and the sliding friction coefficant is 0.10.
a. What does the sled weigh?
W = mg
W = (50)(9.8) = 490N
b. What force will be needed to start the sled moving?(NOTE, You need to use the Coefficent of static friction until it is moving, then you can use the coefficant of kinetic friction)
c. What force is needed to keep the sled moving at a constant velocity?
d. Once moving, what total force must be applied to the sled to accelerate it 3 m/s^2?
23. A force of 40N accelerates a 5kg block at 6 m/s^2 along a horizontal surface.
a. How large is the frictional force?
b. What is the coefficient of friction?
24. A 200kg crate is pushed horizontally with a force of 700N. If the coefficient of friction is 0.20, calculate the acceleration of the crate.
ans.
25. Safety engineers estimate that an elevator can hold 20 persons of 75kg average mass. The elevator itself has a mass of 500kg. Tensile strength tests show that the cable supporting the elevator can tolerate a maximum force of 29600N. What is the greatest acceleration that the elevator's motor can produce without breaking the cable?
ans.
The total mass here is the mass of the persons plus the mass of the elevator.
Now calculate the weight
Now apply Newton's second Law
26. The instruments attached to a weather balloon have a mass of 5.0kg.
a. The balloon is released, and exerts an upward force of 98N on the instruments. What is the acceleration of the balloon and instruments?
b. After the balloon has been acelerating for 10.0 seconds, the instruments are released. What is the velocity of the instruments at the moment of their release?
c. What net force acts on the instruments after their release?
ans.
The instruments weight -49N
d. When does the direction of their velocity first become downward?
This balloon is going to follow projectile motion, so that when the final velocity become zero, the balloon is at its maximum height. It will then begin to fall down.
27. A 2kg mass (m1) and a 3kg mass (m2) are attached to a lightweight cord that passes over a frictionless pulley, as diagrammed. The hanging masses are free to move. Take the direction of the physical motion, smaller mass upward and larger mass downward, to be the positive direction of motion.
a. Draw the situation, showing all forces.
b. In what direction does the smaller mass move?
ans.
Upward
c. What is the acceleration?
The best way to do this problem is to isolate each mass, then combine them.
m1
m2
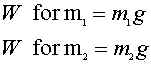
now substitute the what you got for m2 into m1 and solve for a.
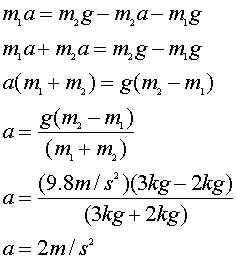
28. You change the masses in previous problem to 1kg and 4kg.
a. What can you expect the acceleration of the 4kg mass to be?
Use the exact same method as above.
b. What is the tension force acting on the cord?
29. You then decide to replace the 1kg object from Problem 28 with a 2kg object
a. What is the acceleration of the 2kg object?
Again this is done the exact same as previous problems.
b. What is the tension force acting on the cord?