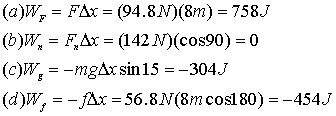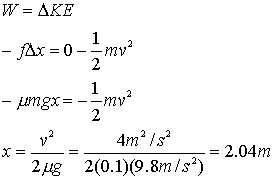
Work and Energy
8-12
8. This is the same type of problem as 7, except as couple of steps. I will do it analytically, but you may want to plug in numbers right away.
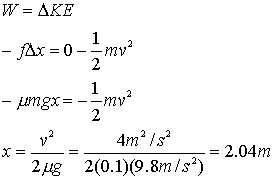
9. First thing to do here is to draw a diagram.
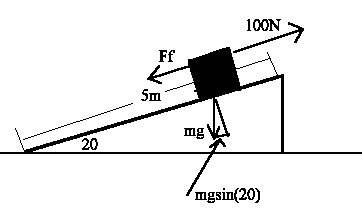
For part a, only the x component of the weight is doing work (mgsin(20)).
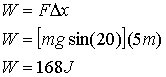
For part b, you need to calculate the frictional force, then calculate the amount of work done by friction, this is the same as change in kinetic energy.
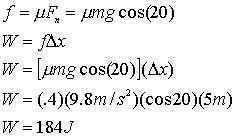
For part c, just use the 100N force to calculat the W.
W=(100N)(5m)=500J
For part d, the change in kinetic energy is equal to the net work done. We can get that by adding up all the individual works.
![]()
For part e, use the change in kinetic energy and solve for the final velocity.
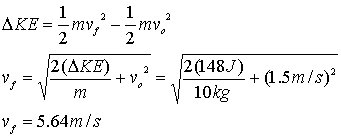
10. Here we know that the total work done is equal to the change in kinetic energy plus the change in the potential energy.

For the second part, you know that it takes 30s to do this work so
![]()
11. The first thing I would do with this problem is to figure out how much energy she dissipate per meter, that way I can just use the power relationship I have.

The result we got is a force. How do you know that? Work is the Force multiplied by the distance. If you solve for Force, you get energy/distance. That is what you have here. Now calculate the velocity using power.

12. First thing to do here is to draw the diagram
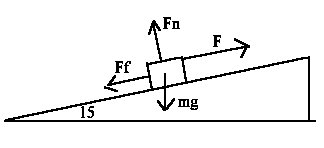
Now apply Newton's second law to see what the value of your forces are.
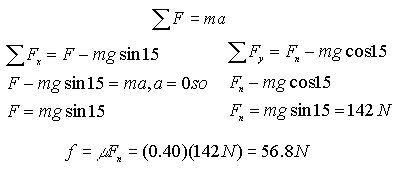
Now go get the work for all the different forces